Every time you open a secure website (https://…), you trust that your data is protected. But have you ever wondered how HTTPS actually works behind the scenes?
Let’s break it down step-by-step 👇
⸻
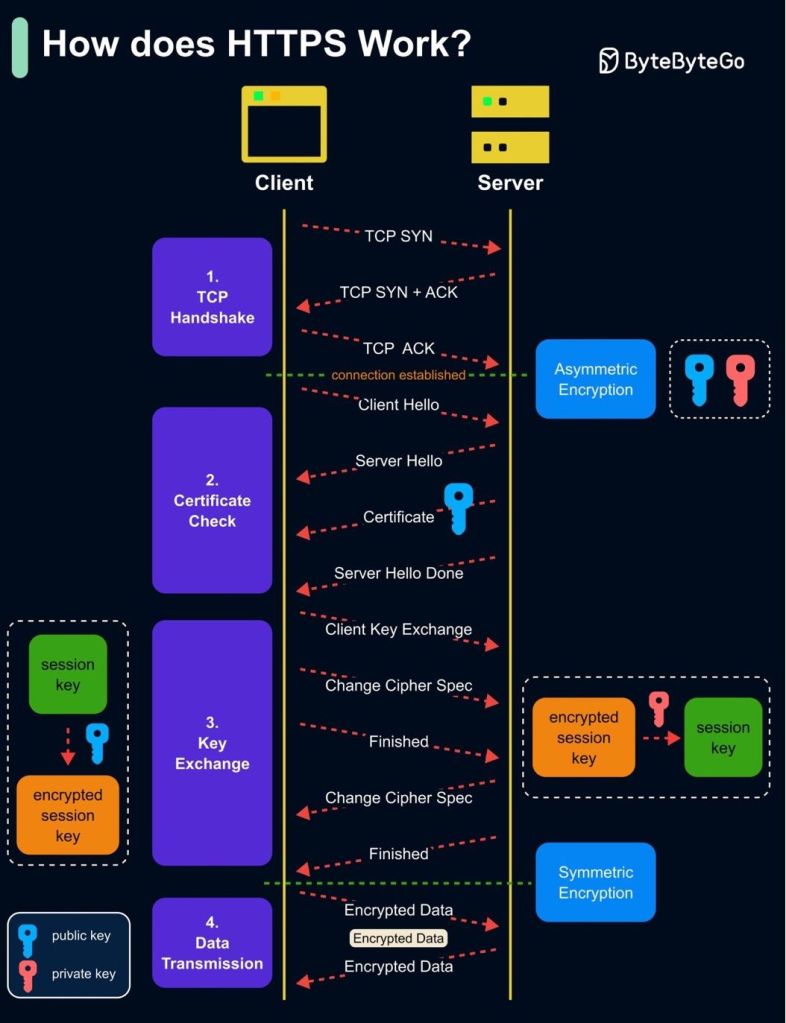
🧩 1. Server Certificate Check
• The client (your browser) and the server exchange “HELLO” messages to start the handshake.
• The server sends its digital certificate (SSL/TLS cert), which includes its public key.
• The client verifies the certificate using a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) to ensure it’s authentic and untampered.
📌 Purpose: Authentication & trust establishment
⸻
🔐 2. Key Exchange (TLS Handshake)
• The client generates a random session key (used for symmetric encryption).
• It encrypts this session key using the server’s public key and sends it over.
• Only the server can decrypt it with its private key.
📌 Purpose: Securely share a common encryption key over an insecure network
⸻
📡 3. Encrypted Tunnel for Data Transmission
• Now both client and server share the same symmetric session key.
• All further communication is encrypted using this session key.
• This ensures fast and secure data exchange.
📌 Purpose: Ensure confidentiality, integrity, and performance during data transfer
⸻
✅ Result:
A secure, encrypted tunnel that protects your data from eavesdropping, man-in-the-middle attacks, and tampering.
⸻
💡 Next time you see the 🔒 icon in your browser, remember there’s a powerful cryptographic handshake happening in milliseconds to keep your data safe.

Leave a comment