By Abhishek Kumar — Azure Expert | Technical Architect
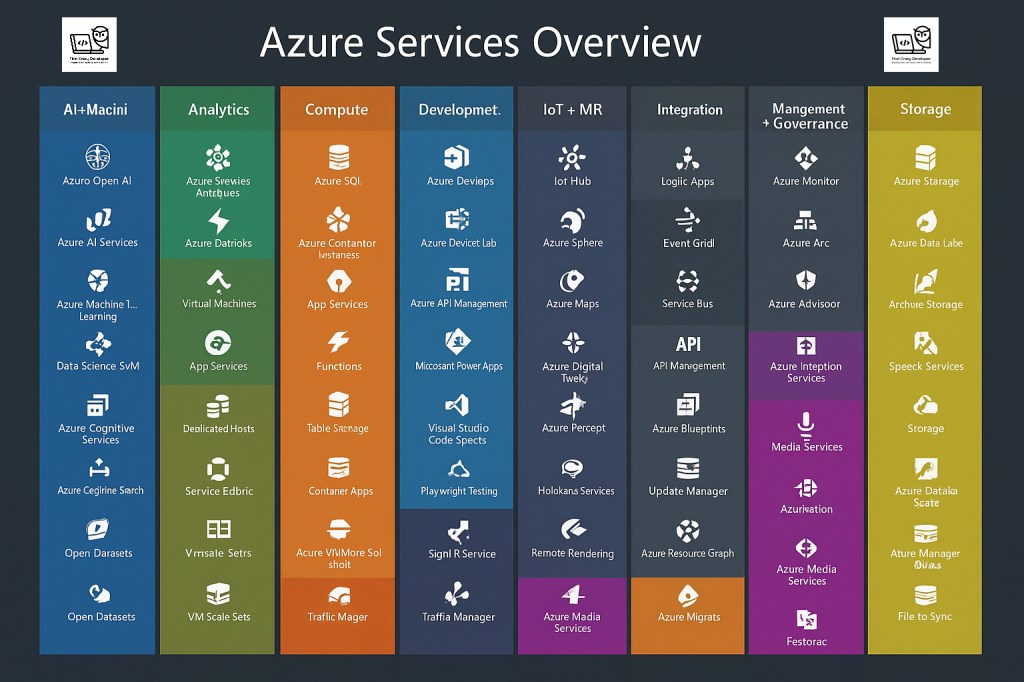
Microsoft Azure is one of the most comprehensive cloud platforms today. With hundreds of services available, this visual map categorizes the core Azure services into understandable groups. Let’s explore each service from the image, understand what it does, and where it fits in the real world.
🔵 AI + Machine Learning
1. Azure OpenAI
- What: Offers large language models like GPT through Azure.
- When to Use: Customer service bots, content summarization, and intelligent search.
- Example: Building a virtual assistant in a banking app.
2. Azure AI Services
- What: Prebuilt APIs for vision, speech, and language tasks.
- When to Use: Facial recognition, translation, sentiment analysis.
- Example: Analyzing customer reviews for emotion detection.
3. Azure Machine Learning
- What: A managed service for building, training, and deploying ML models.
- When to Use: Custom AI workflows using Python, R, or notebooks.
- Example: Predictive maintenance in manufacturing.
4. Data Science VM
- What: A pre-configured VM with popular ML libraries.
- When to Use: When data scientists need an environment with Jupyter, RStudio, etc.
- Example: Running deep learning experiments for healthcare data.
5. Azure Cognitive Services
- What: APIs for speech, vision, decision, and language.
- When to Use: Automating document processing, video indexing.
- Example: Reading invoices automatically.
6. Azure Cognitive Search
- What: Search-as-a-service with AI integration.
- When to Use: When you want Google-like search for your own app data.
- Example: Searching products in an e-commerce catalog.
7. Open Datasets
- What: Publicly available datasets optimized for ML training.
- When to Use: For prototyping and training ML models quickly.
- Example: Training an urban traffic prediction model.
🟢 Analytics
1. Azure Synapse Analytics
- What: Unified analytics platform combining data warehouse and big data.
- When to Use: For enterprise-scale analytics across silos.
- Example: Generating business intelligence dashboards for CFOs.
2. Azure Databricks
- What: Apache Spark-based analytics platform optimized for Azure.
- When to Use: For real-time streaming and large data processing.
- Example: Processing IoT sensor data for fleet analytics.
3. Virtual Machines
- What: Infrastructure-as-a-service for running Windows/Linux VMs.
- When to Use: Custom apps that need full OS control.
- Example: Hosting legacy ERP applications.
4. App Services (Web Apps)
- What: PaaS for hosting web apps and APIs.
- When to Use: Quick deployment of websites with autoscaling.
- Example: Hosting a customer portal with minimal server management.
5. Dedicated Hosts
- What: Provides physical servers dedicated to your organization.
- When to Use: For compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Example: Financial institutions needing hardware isolation.
6. Service Fabric
- What: Microservices platform for scalable, distributed apps.
- When to Use: Complex stateful services like messaging and games.
- Example: Building an online multiplayer game backend.
7. VM Scale Sets
- What: Auto-scaling sets of identical VMs.
- When to Use: High-load apps with elastic scaling needs.
- Example: Hosting an online sale event.
🟠 Compute
1. Azure SQL
- What: Managed SQL Server database engine.
- When to Use: Any application that needs relational data storage.
- Example: Backend of an inventory management app.
2. Azure Container Instances
- What: Run containers without managing VMs or orchestration.
- When to Use: Short-lived jobs or batch processing in containers.
- Example: Processing files uploaded to blob storage.
3. App Services
- (Same as above in Analytics)
4. Azure Functions
- What: Serverless compute for running event-driven code.
- When to Use: Lightweight tasks like file processing, API triggers.
- Example: Resizing images when uploaded.
5. Table Storage
- What: NoSQL key-value storage.
- When to Use: Storing structured but non-relational data.
- Example: IoT device logs or metadata.
6. Container Apps
- What: Serverless containers with scaling and traffic management.
- When to Use: Microservices without full Kubernetes setup.
- Example: A simple booking service that scales with users.
7. VM Image Solutions
- What: Custom images for VM deployment.
- When to Use: Deploying pre-configured apps or environments.
- Example: Company-wide virtual desktop with apps installed.
8. Traffic Manager
- What: DNS-based load balancing.
- When to Use: To route users to nearest or healthiest endpoint.
- Example: Directing global users to nearest website version.
🔷 Development
1. Azure DevOps
- What: CI/CD pipelines, Git repos, boards, testing.
- When to Use: End-to-end DevOps lifecycle management.
- Example: Automating deployment of microservices.
2. DevTest Labs
- What: Provisioning VMs for test/dev at low cost.
- When to Use: Quickly spinning up environments for QA teams.
- Example: A sandbox for interns to learn app deployment.
3. API Management
- What: Gateway for publishing, securing, and managing APIs.
- When to Use: When exposing backend APIs to clients or partners.
- Example: Exposing product catalog API to retailers.
4. Power Apps
- What: Low-code app development platform.
- When to Use: Rapid business process automation without full coding.
- Example: Employee leave approval workflow app.
5. Visual Studio Code Spaces
- What: Cloud-based development environments.
- When to Use: Remote development from browser.
- Example: Quick collaboration on an urgent bugfix.
6. Playwright Testing
- What: UI automation testing framework.
- When to Use: Validating browser apps automatically.
- Example: End-to-end testing of an e-commerce checkout flow.
7. SignalR
- What: Real-time messaging for web apps.
- When to Use: Chat apps, live dashboards, notifications.
- Example: A live auction platform.
8. Traffic Manager
- (Repeated; see Compute)
🟣 IoT + MR
1. IoT Hub
- What: Central hub for device communication.
- When to Use: For bidirectional IoT device communication.
- Example: Managing 1000s of connected thermostats.
2. Azure Sphere
- What: Secure microcontroller + OS for devices.
- When to Use: Embedded device security and connectivity.
- Example: Secure vending machines or elevators.
3. Azure Maps
- What: Geospatial APIs and mapping services.
- When to Use: Apps needing navigation, routing, or maps.
- Example: Delivery tracking for logistics.
4. Azure Digital Twins
- What: Models real-world systems digitally.
- When to Use: To simulate smart buildings, factories.
- Example: Monitoring HVAC systems in real-time.
5. Azure Percept
- What: Vision and voice AI at the edge.
- When to Use: Smart retail, factory floor vision.
- Example: Detecting defective products on assembly line.
6. HoloLens Services
- What: Platform for mixed reality applications.
- When to Use: Training, design, or field service assistance.
- Example: Remote support in oil rigs using MR headset.
7. Remote Rendering
- What: Renders 3D content in the cloud for HoloLens.
- When to Use: Large CAD or BIM model visualization.
- Example: Engineering walkthrough of architectural designs.
⚫ Integration
1. Logic Apps
- What: Workflow automation through visual designer.
- When to Use: Integrating services with triggers and actions.
- Example: Auto-email invoice when a sale happens.
2. Event Grid
- What: Event routing platform for event-driven architecture.
- When to Use: Publish-subscribe models.
- Example: Notifying services when a blob is created.
3. Service Bus
- What: Enterprise-grade messaging system.
- When to Use: Messaging between distributed systems.
- Example: Retail order system decoupling front and backends.
4. API Management
- (Covered in Development)
5. Blueprints
- What: Governance templates for resource setup.
- When to Use: Standardizing Azure deployments.
- Example: Enforcing tagging, security policies by default.
6. Update Manager
- What: Central patch management.
- When to Use: Managing OS patching for VMs.
- Example: Compliance patching across 200 VMs.
7. Resource Graph
- What: Query-based inventory and insights.
- When to Use: Exploring Azure resource metadata at scale.
- Example: Listing all resources missing tags.
🟡 Storage
1. Azure Storage
- What: General-purpose object, file, and queue storage.
- When to Use: Uploading files, logs, backups.
- Example: Static website hosting.
2. Azure Data Lake
- What: Scalable data lake for analytics.
- When to Use: Big data storage for batch or stream processing.
- Example: Storing logs from millions of IoT devices.
3. Archive Storage
- What: Cold-tier blob storage.
- When to Use: Data accessed rarely.
- Example: Compliance documents stored for 7+ years.
4. Speech Services
- (Duplicate/misplaced in chart — should be under AI)
5. Data Catalog / Scanner
- What: Metadata discovery and classification.
- When to Use: Organizing enterprise data assets.
- Example: Tracking ownership of sensitive data sets.
6. Storage Explorer
- What: GUI tool to interact with Azure storage.
- When to Use: Browsing containers, blobs, and queues.
- Example: Downloading backups from blob storage.
7. File Sync
- What: Sync on-prem file servers with Azure Files.
- When to Use: Hybrid cloud file sharing.
- Example: Branch office file sharing with cloud backup.
✅ Final Words
This updated Azure Services Overview acts as your navigation chart through the complex but powerful Azure ecosystem. Whether you’re building AI-powered apps, deploying microservices, or securing hybrid networks, this map helps you know what to use and when.
📌 Save it.
📊 Share it with your team.
🚀 Use it to accelerate your cloud journey.
💡 Abhishek’s Take:
“In my 14+ years of experience with Azure and Microsoft technologies, I’ve often seen teams struggle not because of lack of tools — but lack of clarity on which tools to use, and when.
This blog solves that. Whether you’re launching your startup or modernizing enterprise IT, this service map + real-world context = pure gold for your cloud journey.”#Azure #MicrosoftAzure #AzureServices #CloudComputing #CloudArchitecture #AzureDevOps #AIonAzure #IoT #AKS #Serverless #DataEngineering #AzureFunctions #TechBlog #AbhishekOnCloud #CloudCareers

Leave a comment