by Abhishek Kumar | FirstCrazyDeveloper
Generative AI (GenAI) has been evolving rapidly. What started as simple text generators is now becoming intelligent, task-oriented systems that can collaborate, plan, and act.
But how exactly did we get here?
Let’s break it down step by step, looking at the progression from LLMs to Agentic AI—and why AI Agents are where things start to get really practical.
1. LLM (Large Language Model) – The Beginning
What it does:
- Produces text based only on the input prompt.
- Works on static knowledge trained before deployment.
Why it’s useful:
- Fast & simple – Great for drafting emails, answering basic questions, or generating creative text.
- Easy to deploy – Minimal setup needed.
Limitations:
- No live knowledge – Can’t access new data.
- No context awareness – Responses are limited to what it has been trained on.
Examples:
- Chatbots
- Email drafting tools
2. RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) – Smarter with Knowledge
What it does:
- Combines LLMs with real-time retrieval of external information.
- Gives accurate and updated answers by pulling data from databases, APIs, or documents.
Why it’s useful:
- Perfect for Q&A or tasks requiring up-to-date information.
- More accurate than LLM-only responses.
Limitations:
- Dependent on data quality – If the source is poor, results suffer.
- Still lacks full autonomy—can’t execute tasks.
Examples:
- Domain-specific assistants (e.g., legal, medical Q&A)
- Knowledge bots fetching live information
3. AI Agents – The Game Changer
This is where things get practical and exciting.
What it does:
- Goes beyond just generating text—it plans, reasons, and acts.
- Can use tools, store memory, and execute multi-step workflows autonomously.
Why it’s useful:
- Perfect for goal-oriented tasks – e.g., research automation, document processing, or orchestrating multiple tools.
- Works like a personal assistant that can make decisions and take action.
Limitations:
- Needs well-defined goals and proper tool setup.
Examples:
- AI-powered research assistants
- Automated workflow bots
- Task planners using reasoning
4. Agentic AI – The Next Frontier
What it does:
- Introduces multiple agents that work together.
- Agents collaborate, negotiate, and share knowledge to tackle complex problems.
Why it’s useful:
- Scales to big tasks – Multiple agents divide labor and handle specialized roles.
- Adaptive & persistent – Retains memory and evolves strategies over time.
Limitations:
- Harder to design & control – Requires advanced architecture and governance.
Examples:
- Multi-agent research teams
- Complex process automation
- AI-driven project management
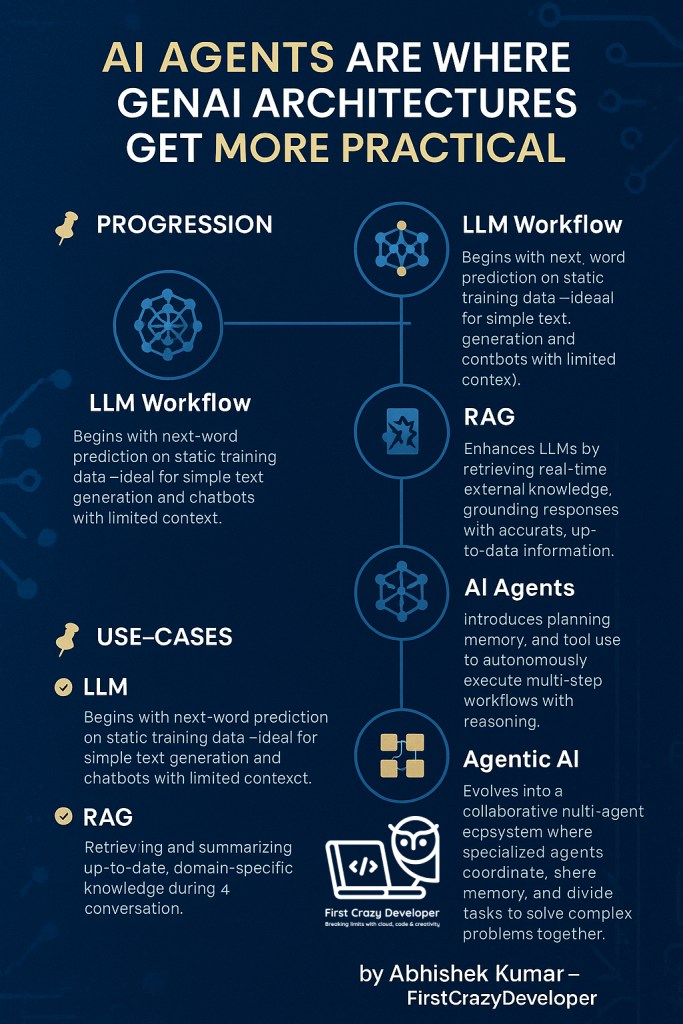
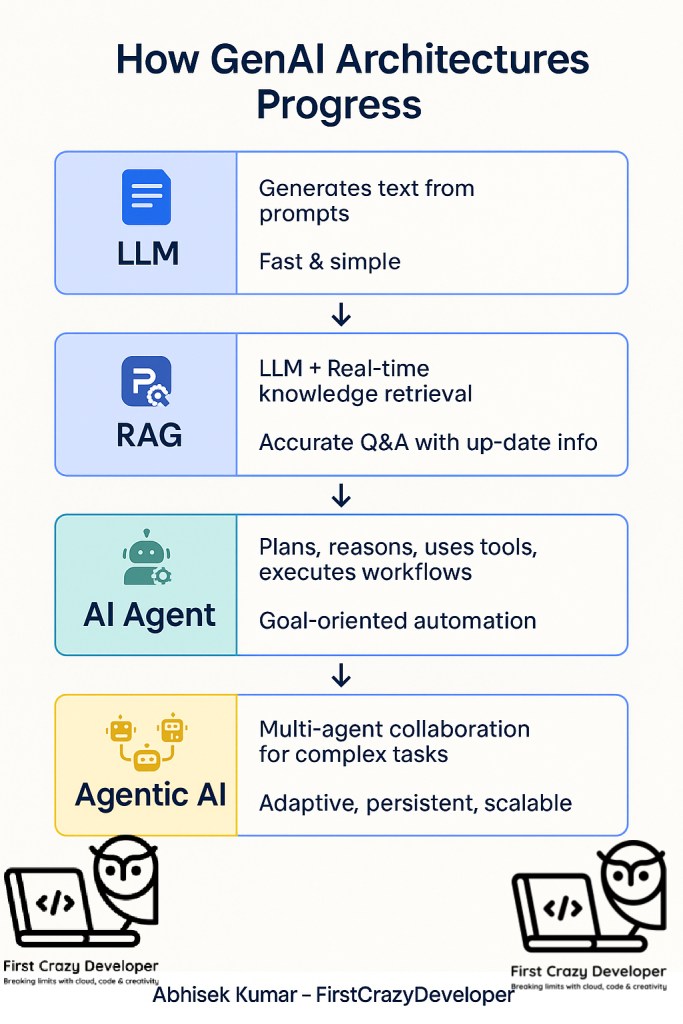
How It All Fits Together (Progression)
- LLM Workflow – Text generation based on static knowledge.
- RAG – Adds real-time knowledge retrieval for smarter responses.
- AI Agents – Introduce reasoning, planning, and tool usage to perform tasks autonomously.
- Agentic AI – Evolves into a multi-agent ecosystem for handling large-scale, collaborative, and adaptive workflows.
Which One Should You Choose?
- LLM: For basic text tasks (chatbots, email drafts).
- RAG: For accurate Q&A needing live or domain-specific data.
- AI Agent: For single-user workflows that require planning and tool execution.
- Agentic AI: For complex, multi-step, multi-agent operations with ongoing collaboration.
Why AI Agents Are the Turning Point
LLMs were a breakthrough. RAG made them smarter. But AI Agents make GenAI practical.
They don’t just talk—they act. They can:
- Plan and execute workflows
- Use tools and access data
- Store memory and learn from feedback
This makes them incredibly powerful for real-world use cases like research assistance, business process automation, and decision-making support.
In short:
- LLMs talk.
- RAGs talk smarter.
- AI Agents act.
- Agentic AI collaborates and scales.
As GenAI systems evolve, AI Agents are where theory turns into practical, real-world impact.
Real-World Examples for Each Stage
LLM (Large Language Model):
- Chatbots for customer support (e.g., ChatGPT, Intercom AI bots).
- Content generation for blogs, social media, and reports.
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation):
- Legal assistants that fetch case laws and generate summaries.
- Healthcare support bots retrieving up-to-date medical guidelines.
AI Agent:
- Research assistants that gather data, summarize insights, and draft reports.
- Automated workflow bots managing tasks like data entry, report generation, and scheduling.
Agentic AI:
- AI-powered project managers coordinating tasks across multiple teams.
- Multi-agent financial analysts collaborating to evaluate investments with live market data.
#GenerativeAI #AIAgents #RAG #AgenticAI #Automation #AI #FirstCrazyDeveloper #AbhishekKumar


Leave a comment