by Abhishek Kumar | FirstCrazyDeveloper
Think of Kubernetes as the brain that runs and manages your containers.
But just like a brain, it needs eyes, ears, arms, and a security system — and that’s where these tools come in.
The Kubernetes ecosystem is massive. Hundreds of tools are available, each designed to solve a very specific problem. If you’ve ever felt overwhelmed by the sheer volume of choices, this guide is for you.
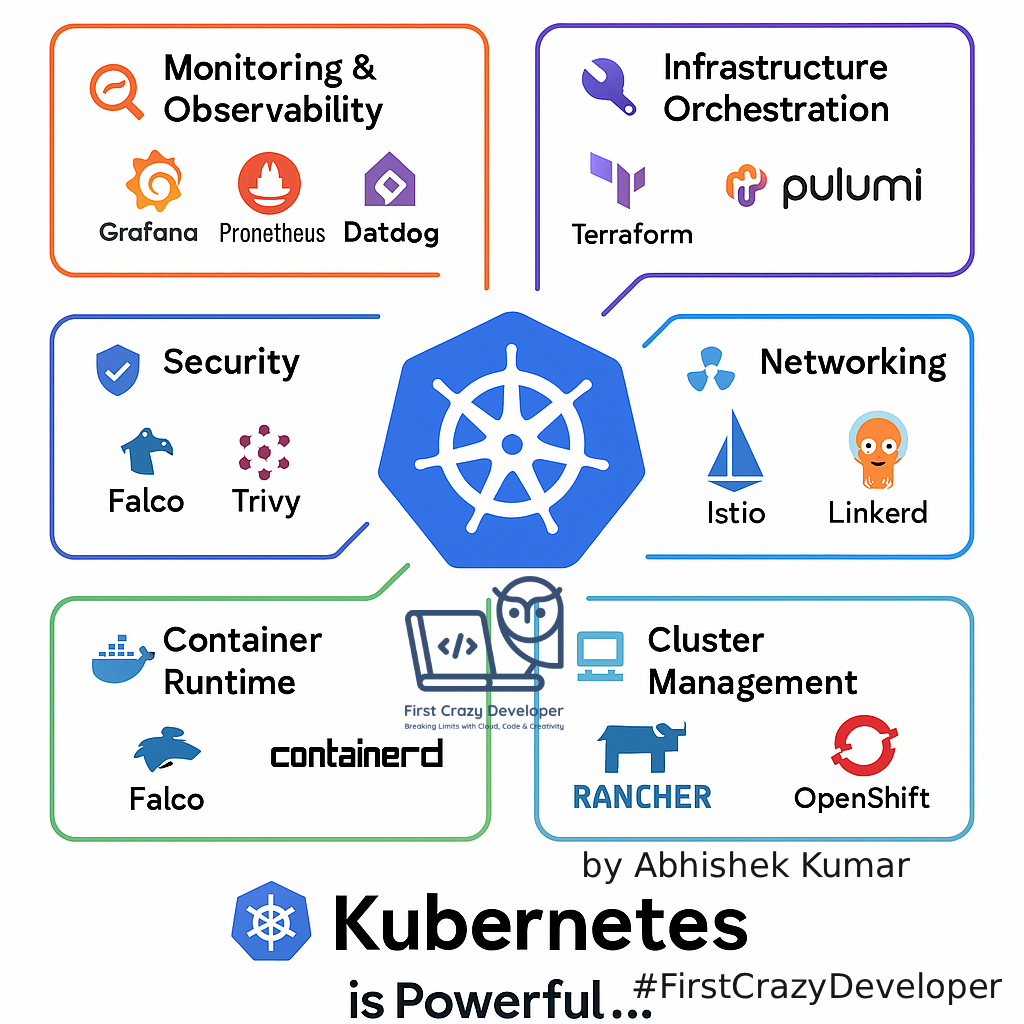
Let’s break it down into six essential categories developers should know:

🔎 1. Monitoring & Observability
Your cluster is only as good as your ability to understand what’s happening inside it.
- Grafana → A powerful data visualization tool that allows you to build rich, interactive dashboards to visualize metrics collected from various sources. Grafana supports a wide range of data sources, making it easy to create comprehensive dashboards tailored to your specific needs.
- Prometheus →A leading open-source monitoring solution that collects and stores time-series data. Prometheus excels at capturing metrics from your Kubernetes cluster and applications, enabling you to set up alerts and monitor performance trends over time.
- Datadog → A cloud-native monitoring platform that provides real-time visibility into your entire infrastructure, including your Kubernetes clusters. Datadog offers a comprehensive suite of features, including monitoring, logging, and security, making it a valuable tool for managing complex environments.
- Jaeger / Zipkin → Distributed tracing tools that help you trace requests across microservices. Jaeger and Zipkin enable you to identify performance bottlenecks and understand the flow of requests through your application, making it easier to troubleshoot issues and optimize performance.
👉 With these tools, you’ll spot issues before they hit production, not after.
⚙️ 2. Infrastructure Orchestration
Deploying Kubernetes is one thing; scaling it without breaking things is another.
- Terraform → An infrastructure-as-code tool that allows you to define and manage your infrastructure in a declarative manner. Terraform supports a wide range of cloud providers and services, making it easy to provision and manage resources across different environments.
- Pulumi → Another infrastructure-as-code tool that allows you to write infrastructure definitions in familiar programming languages such as Python, JavaScript, and Go. Pulumi offers a more flexible and expressive way to define your infrastructure compared to traditional configuration languages.
- Argo CD → A GitOps-based Kubernetes deployment automation tool that automates the deployment and management of applications based on Git repositories. Argo CD ensures that your Kubernetes deployments are always in sync with your desired state, as defined in your Git repository.
👉 Think of these as your automation wizards that save you from endless manual setups.
🌐 3. Networking
For microservices, networking is everything. Without it, your apps are just isolated islands.
- Istio → A service mesh that provides traffic routing, security, and observability for your microservices. Istio simplifies the management of complex microservice architectures by providing features such as traffic management, security policies, and monitoring.
- Linkerd → A lightweight service mesh that offers similar functionality to Istio but with a simpler architecture and lower overhead. Linkerd is a good choice for organizations that need a service mesh but want to avoid the complexity of Istio.
- Traefik → A smart ingress controller that makes routing traffic to your Kubernetes services effortless. Traefik automatically configures itself based on your Kubernetes resources, making it easy to expose your services to the outside world.
👉 These ensure your services communicate smoothly and securely.
🖥️ 4. Cluster Management
Running a single Kubernetes cluster locally is easy. Running multiple clusters in production? That’s a headache.
- Minikube → A tool that allows you to spin up a lightweight Kubernetes cluster for local development and testing. Minikube is a great way to experiment with Kubernetes and test your applications before deploying them to a production environment.
- Rancher → A centralized management platform for multiple Kubernetes clusters. Rancher provides a single pane of glass for managing all of your Kubernetes clusters, making it easier to monitor their health, deploy applications, and enforce security policies.
- OpenShift → An enterprise-ready Kubernetes platform that includes a comprehensive set of developer tools and features. OpenShift is designed to simplify the development, deployment, and management of containerized applications in enterprise environments.
👉 These tools help you create, manage, and upgrade clusters without losing sleep.
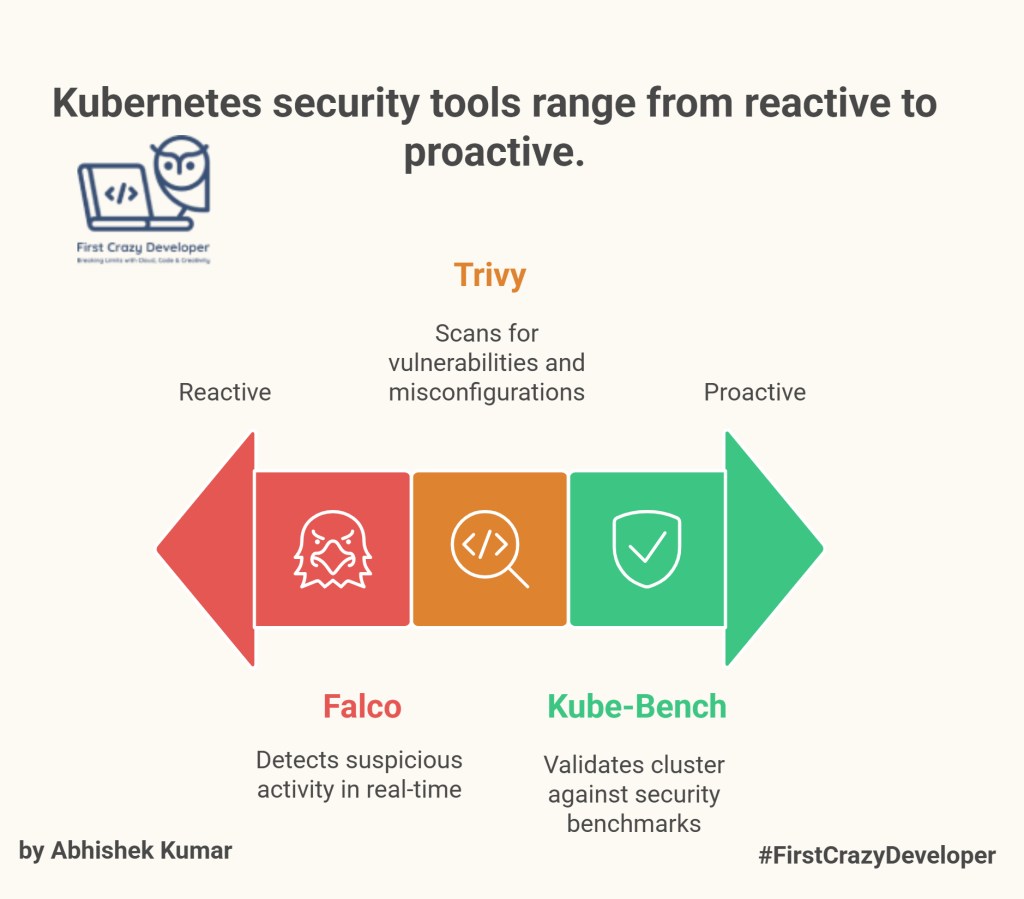
🛡️ 5. Security
Kubernetes is powerful, but it’s also a hacker’s dream if not properly secured.
- Falco → A real-time threat detection tool for containers. Falco monitors your Kubernetes cluster for suspicious activity and alerts you to potential security threats.
- Trivy → A vulnerability scanner that scans your container images and Kubernetes configurations for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. Trivy helps you identify and remediate security issues before they can be exploited.
- Kube-Bench → A tool that validates your Kubernetes cluster against security benchmarks such as the CIS Kubernetes Benchmark. Kube-Bench helps you ensure that your Kubernetes cluster is configured securely and meets industry best practices.
👉 They act like your bodyguards, ensuring no intruder sneaks in.
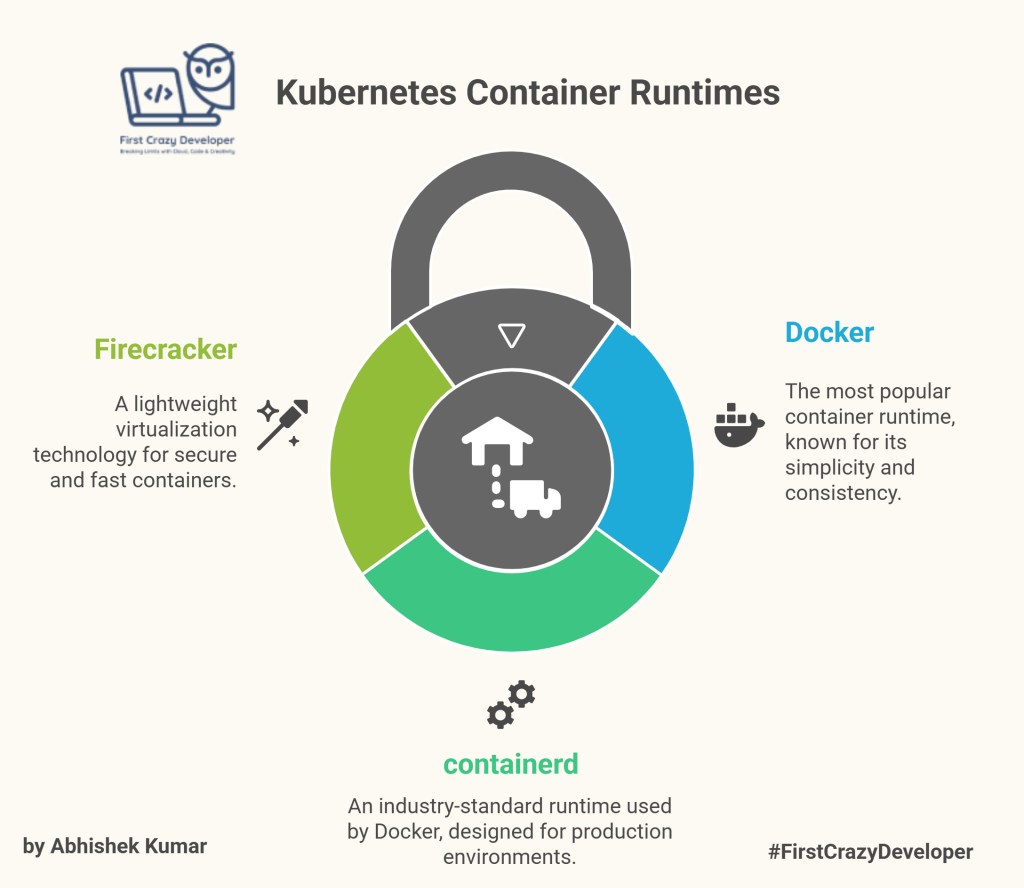
📦 6. Container Runtime
At the end of the day, Kubernetes needs something to actually run your containers.
- Docker → The most popular container runtime. Docker provides a simple and consistent way to package and run applications in containers.
- containerd → An industry-standard container runtime that is used by Docker itself. Containerd is a lightweight and efficient container runtime that is designed for production environments.
- Firecracker →A lightweight virtualization technology that enables you to run secure and fast containers. Firecracker is designed for serverless workloads and provides strong isolation between containers.
👉 These are the engines under the hood, powering your workloads.
💡Wrapping Up
Kubernetes is the engine.
These tools? They’re the pit crew keeping it running at top speed.
As a developer or architect, you don’t need to master everything at once. Instead:
- Pick one category that aligns with your current challenges.
- Go deep.
- Then expand your toolkit as your Kubernetes journey matures.
💡 If you had to master just one category of Kubernetes tools this year…
👉 Which one would you choose?
#Kubernetes #CloudComputing #DevOps #Containerization #CloudNative #Microservices #Docker #InfrastructureAsCode #Observability #Security #FirstCrazyDeveloper #AbhishekKumar

Leave a comment