✍️ Abhishek Kumar | #FirstCrazyDeveloper
When building large-scale systems, the challenge isn’t just about writing clean code—it’s about designing for scale, resilience, and performance. This is where system design heuristics come into play. They act as guiding principles to make smart decisions when architecting software.
In this blog, we’ll break down 15 key heuristics, explain their importance, and show real-world examples so you can apply them in your own projects.
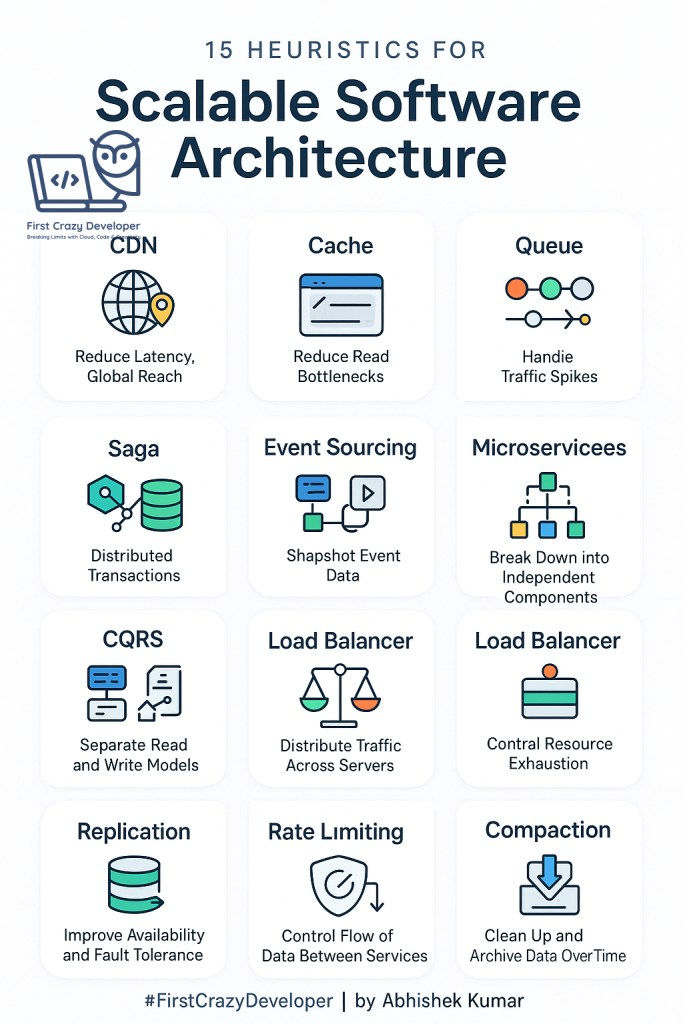
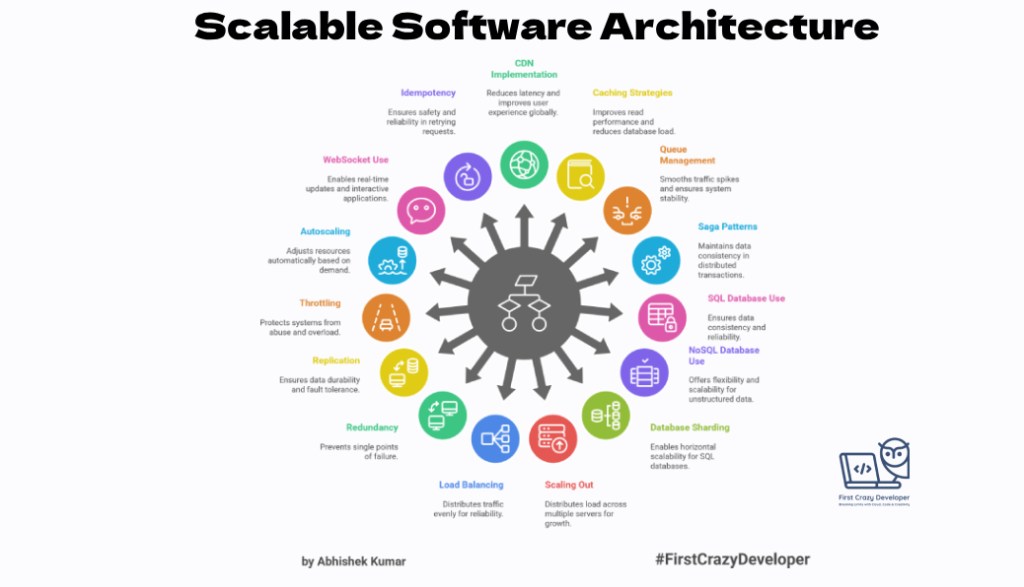
1. CDN (Content Delivery Network) → Latency + Global
CDNs place cached content closer to users worldwide, reducing latency.
- Example: Netflix uses CDNs so you don’t buffer movies even if you’re in Amsterdam while the main server is in the U.S.
- Takeaway: Use CDNs for static assets like images, videos, and CSS/JS files when building global apps.
2. Cache → Read + Bottleneck
Caches reduce the load on primary databases by storing frequently accessed data.
- Example: Twitter caches trending hashtags to avoid hitting the database millions of times per second.
- Takeaway: Cache hot data (like session tokens, product catalogs) to remove bottlenecks.
3. Queue → Write + Spike
Queues smooth out traffic spikes by decoupling producers and consumers.
- Example: Uber uses message queues when riders request trips. Instead of overloading the system, requests are queued and processed asynchronously.
- Takeaway: Introduce queues for asynchronous tasks like payment processing, notifications, or email sending.
4. Saga → Distributed + Transaction
When a single transaction spans multiple microservices, sagas help maintain consistency.
- Example: Booking a flight + hotel + car rental on Expedia. If one step fails, compensating transactions (refunds/cancellations) roll back the flow.
- Takeaway: Implement Saga patterns in microservices to handle distributed transactions.
5. SQL → ACID + Relational
SQL databases ensure atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability.
- Example: Banking systems use SQL to ensure your account is debited only if the recipient’s account is credited.
- Takeaway: Choose SQL for critical data requiring strict consistency.
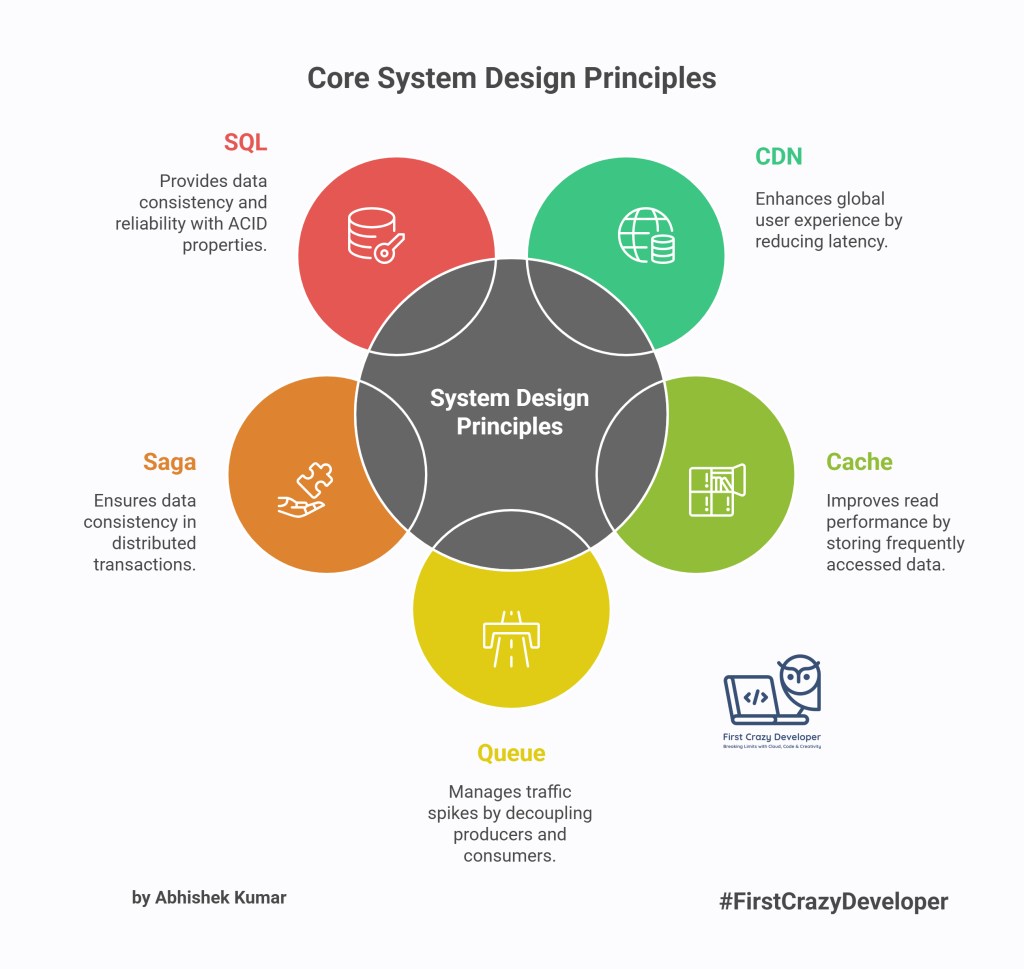
6. NoSQL → Flexible + Scale
NoSQL databases trade strict consistency for flexibility and horizontal scalability.
- Example: Instagram stores billions of photos in NoSQL databases like Cassandra.
- Takeaway: Use NoSQL for unstructured data like logs, user profiles, or IoT data.
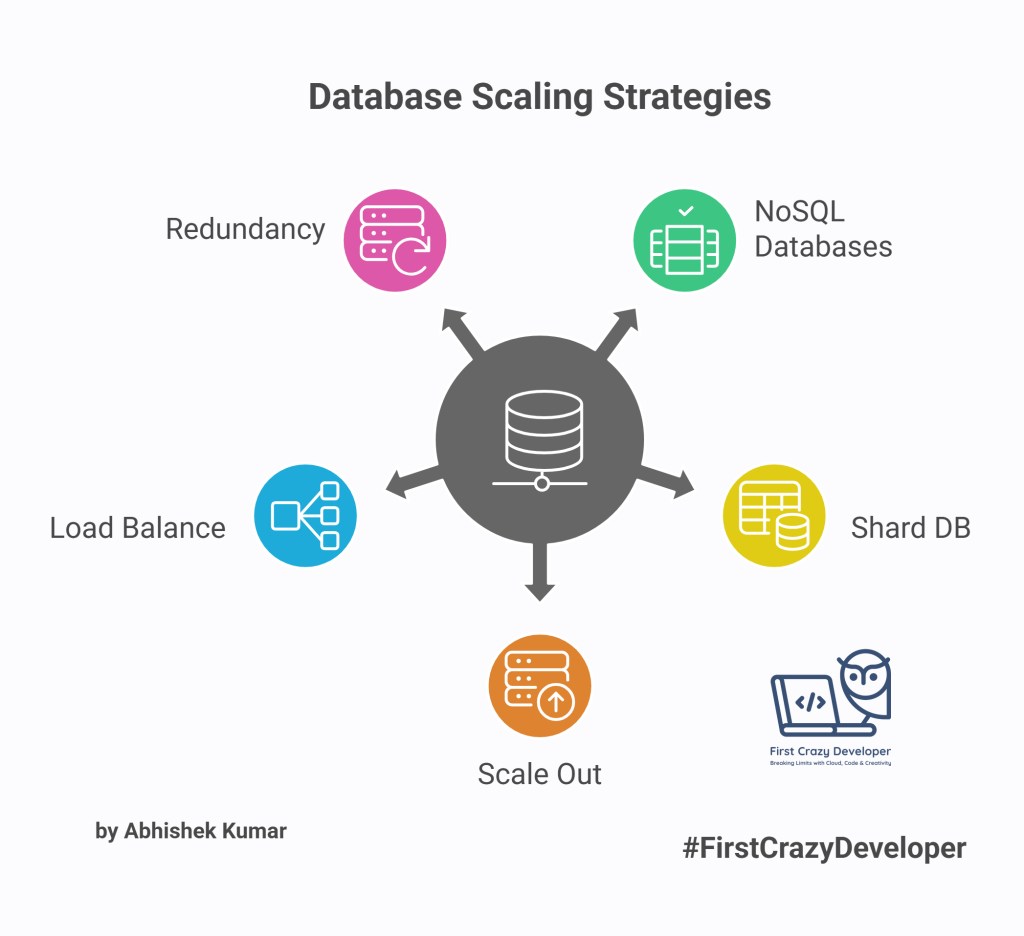
7. Shard DB → SQL + Scale
Sharding splits a large database into smaller, manageable pieces.
- Example: Facebook shards its user database by user ID ranges to scale horizontally.
- Takeaway: Use sharding when SQL alone cannot handle massive data.
8. Scale Out → Load + Growth
Scaling out means adding more servers instead of making one server stronger.
- Example: Amazon adds hundreds of servers during Black Friday sales.
- Takeaway: Always design with horizontal scaling in mind.
9. Load Balance → Traffic + Reliability
Load balancers distribute requests evenly to prevent server overload.
- Example: Google Search uses global load balancers to route billions of requests daily.
- Takeaway: Use load balancing to improve reliability and high availability.
10. Redundancy → Core + Failure
Adding redundant systems prevents single points of failure.
- Example: Airplanes have redundant engines so one failure doesn’t cause a crash. Similarly, AWS runs multiple availability zones.
- Takeaway: Add redundancy at critical layers—servers, databases, and network.
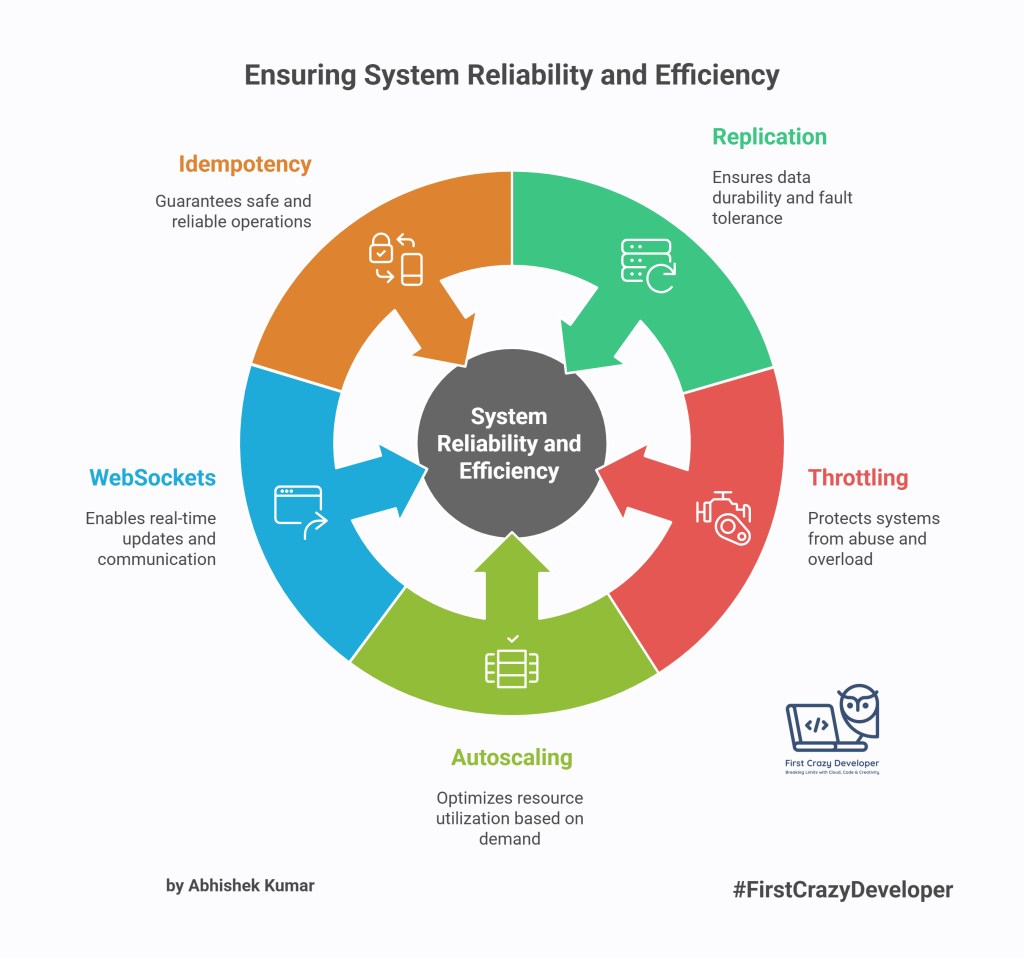
11. Replication → Durability + Faults
Replication ensures copies of data exist across regions to avoid loss.
- Example: WhatsApp messages are replicated so you don’t lose chats if a server goes down.
- Takeaway: Replicate across regions for disaster recovery.
12. Throttle → Requests + Spike
Throttling limits requests to protect systems from abuse or overload.
- Example: GitHub API rate limits requests to prevent misuse.
- Takeaway: Always implement throttling in APIs.
13. Autoscale → Load + Spike
Autoscaling adjusts resources automatically to meet demand.
- Example: Netflix auto-scales servers during peak hours at night.
- Takeaway: Cloud providers (AWS, Azure, GCP) offer auto-scaling—use it to cut costs.
14. WebSockets → Realtime + Updates
WebSockets provide persistent, bidirectional communication.
- Example: WhatsApp web client updates instantly when you receive a message.
- Takeaway: Use WebSockets for chat apps, live dashboards, or stock tickers.
15. Idempotent → Retry + Safety
Idempotent operations guarantee the same result even if repeated.
- Example: Clicking “Pay” twice on Amazon won’t double-charge you because the API ensures idempotency.
- Takeaway: Always design APIs to be idempotent, especially for financial transactions.
💡 Abhishek’s Take
System design is not about memorizing buzzwords—it’s about building mental guardrails that help you make better trade-offs under real-world pressure.
Here’s what I’ve learned from applying these heuristics in real projects:
- Balance is everything. A cache may solve read bottlenecks, but without eviction policies it can introduce stale data. Always measure impact before scaling solutions.
- Fail gracefully. Users forgive slow responses more than system crashes. Queues, retries, and idempotency aren’t just patterns—they’re safety nets for user trust.
- Think global, act local. CDNs, replication, and load balancers aren’t optional when your users are distributed across continents. Latency becomes your invisible enemy.
- Design for growth, not today. A startup’s SQL DB might work now, but sharding, autoscaling, and load balancing should be in your future roadmap.
- Observability is a superpower. Without metrics, logs, and tracing, heuristics are guesses. With observability, they become measurable engineering decisions.
👉 Remember: tools will change—SQL, NoSQL, WebSockets, or even AI-driven infra—but these principles stay timeless. They’re what separate scalable systems from fragile ones.
🔑 Final Thoughts
System design heuristics are not hard rules—they’re battle-tested patterns that help you make better decisions. Whether you’re preparing for interviews or designing production systems, these 15 heuristics provide a solid foundation.
By combining caching, queues, autoscaling, and idempotent APIs, you can build systems that are scalable, resilient, and user-friendly—the three pillars of modern engineering.
#SystemDesign #CloudComputing #Azure #SoftwareArchitecture #Scalability #FirstCrazyDeveloper #TechBlog #Engineering

Leave a comment