✍️ Abhishek Kumar | #FirstCrazyDeveloper
APIs are the backbone of modern applications, enabling different systems, services, and devices to communicate seamlessly. Over the years, several API protocols and communication styles have emerged, each suited for specific use cases — from mobile apps fetching user data to IoT devices streaming sensor events.
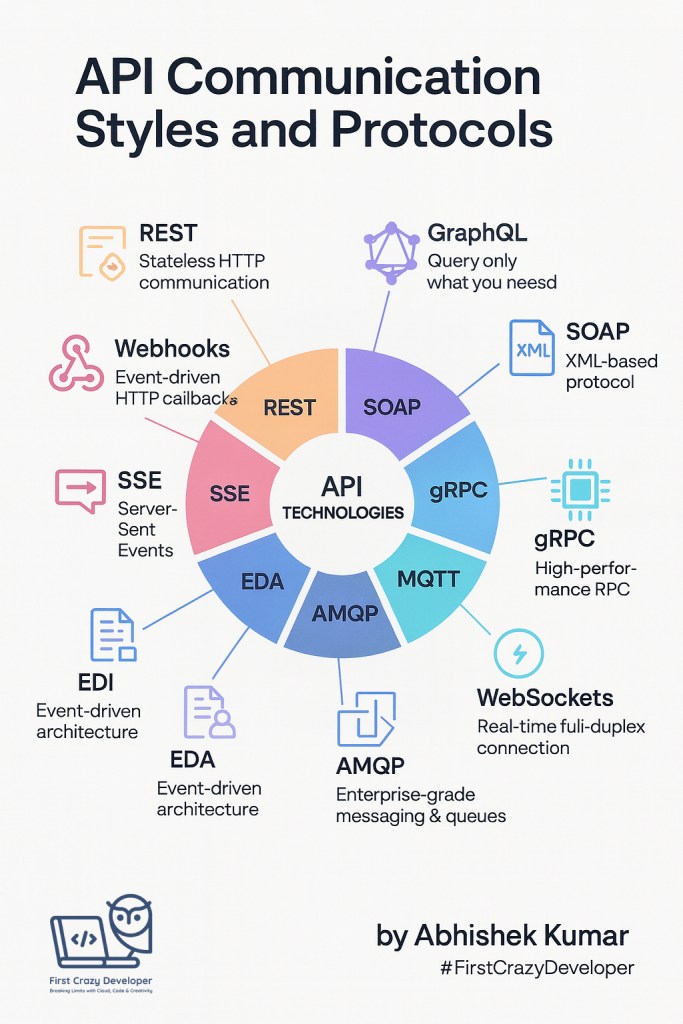
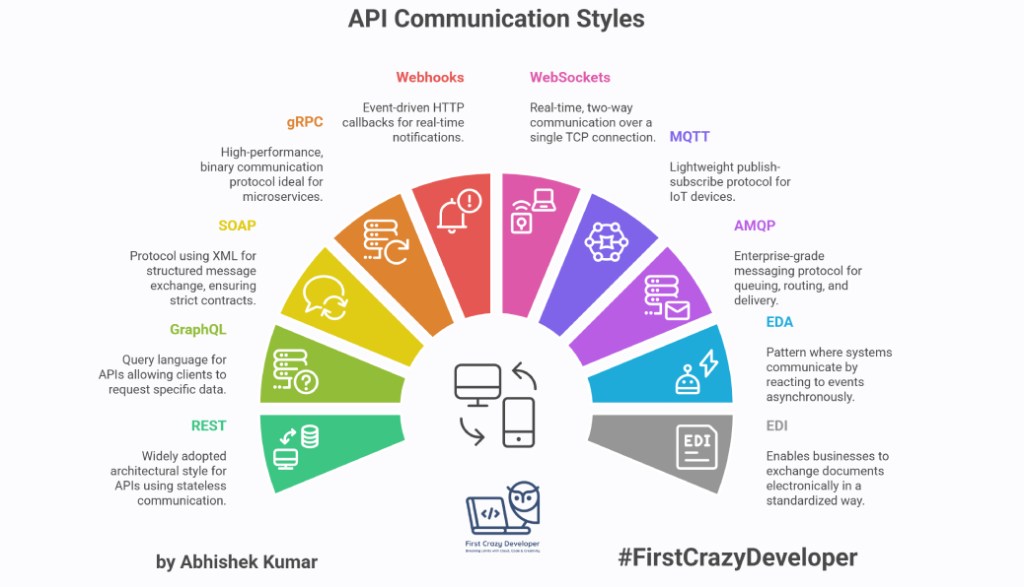
In this blog, let’s explore the 11 major API communication styles and protocols with real-world examples and C# code snippets.
1. REST (Representational State Transfer)
What it is:
REST is the most widely adopted architectural style for APIs. It uses stateless communication where each HTTP request contains all necessary information. Data is typically exchanged in JSON format.
Real-World Example:
- A weather app calling a REST API to fetch the current temperature.
- E-commerce apps using REST endpoints to manage products (
/api/products), orders (/api/orders), etc.
C# Example (Calling REST API):
using System;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
class Program
{
static async Task Main()
{
using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient())
{
HttpResponseMessage response = await client.GetAsync("https://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q=Amsterdam&appid=your_api_key");
string result = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
}
}
2. GraphQL
What it is:
GraphQL is a query language for APIs that lets clients request exactly the data they need. Unlike REST (which may return too much or too little), GraphQL gives flexibility to shape the response.
Real-World Example:
- Facebook (who created GraphQL) uses it in their apps to fetch user profiles, posts, and comments in a single request.
- GitHub GraphQL API allows developers to fetch repositories, issues, and contributors with precise fields.
C# Example (GraphQL Query):
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
class Program
{
static async Task Main()
{
var query = "{ user(login: \"FirstCrazyDeveloper\") { name repositories(last: 2) { nodes { name } } } }";
using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient())
{
var content = new StringContent("{\"query\":\"" + query + "\"}", Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
var response = await client.PostAsync("https://api.github.com/graphql", content);
var result = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
}
}
3. SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol)
What it is:
SOAP is a protocol that uses XML for structured message exchange. It ensures strict contracts and is often used in banking, insurance, and legacy enterprise systems.
Real-World Example:
- Payment gateways (older ones) like PayPal used SOAP for transaction requests.
- Airline booking systems still heavily rely on SOAP.
C# Example (SOAP Client):
// Add Service Reference → Enter WSDL URL
ServiceClient client = new ServiceClient();
var response = client.GetCustomerDetails(123);
Console.WriteLine(response.Name);
4. gRPC (Google Remote Procedure Call)
What it is:
gRPC is a high-performance, binary communication protocol using Protocol Buffers. It’s ideal for microservices that need fast communication.
Real-World Example:
- Netflix uses gRPC for microservices.
- Kubernetes also uses gRPC for cluster communication.
C# Example (gRPC Client):
using Grpc.Net.Client;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
class Program
{
static async Task Main()
{
var channel = GrpcChannel.ForAddress("https://localhost:5001");
var client = new Greeter.GreeterClient(channel);
var reply = await client.SayHelloAsync(new HelloRequest { Name = "Abhishek" });
Console.WriteLine(reply.Message);
}
}
5. Webhooks
What it is:
Webhooks are event-driven HTTP callbacks. When an event occurs, the system sends an HTTP POST request to a predefined URL.
Real-World Example:
- Stripe sends payment confirmation via Webhook.
- GitHub sends repo push notifications to CI/CD pipelines.
C# Example (Webhook Receiver in ASP.NET Core):
[HttpPost("webhook")]
public IActionResult Receive([FromBody] dynamic payload)
{
Console.WriteLine(payload);
return Ok();
}
6. WebSockets
What it is:
WebSockets enable real-time, two-way communication over a single TCP connection. Unlike HTTP, the connection remains open.
Real-World Example:
- WhatsApp Web using WebSockets for real-time chat sync.
- Online trading platforms pushing live stock prices.
C# Example (Client WebSocket):
using System;
using System.Net.WebSockets;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
class Program
{
static async Task Main()
{
using (var ws = new ClientWebSocket())
{
await ws.ConnectAsync(new Uri("wss://echo.websocket.org"), CancellationToken.None);
var bytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("Hello WebSocket!");
await ws.SendAsync(new ArraySegment<byte>(bytes), WebSocketMessageType.Text, true, CancellationToken.None);
}
}
}
7. MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport)
What it is:
MQTT is a lightweight publish-subscribe protocol built for IoT. It works well in constrained devices with poor networks.
Real-World Example:
- Smart home devices (like Alexa, smart bulbs).
- Connected cars streaming sensor data.
C# Example (MQTT Client):
using MQTTnet;
using MQTTnet.Client;
class Program
{
static async Task Main()
{
var factory = new MqttFactory();
var client = factory.CreateMqttClient();
await client.ConnectAsync(new MqttClientOptionsBuilder().WithTcpServer("broker.hivemq.com").Build());
await client.PublishAsync("iot/sensor", "Temperature:25C");
}
}
8. AMQP (Advanced Message Queuing Protocol)
What it is:
AMQP is an enterprise-grade messaging protocol for queuing, routing, and delivery.
Real-World Example:
- RabbitMQ implements AMQP for distributed messaging.
- Banking applications use AMQP for reliable transactions.
C# Example (AMQP with RabbitMQ):
using RabbitMQ.Client;
using System.Text;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
var factory = new ConnectionFactory() { HostName = "localhost" };
using var connection = factory.CreateConnection();
using var channel = connection.CreateModel();
channel.QueueDeclare("queue1", false, false, false, null);
string message = "Hello RabbitMQ!";
var body = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(message);
channel.BasicPublish("", "queue1", null, body);
}
}
9. EDA (Event-Driven Architecture)
What it is:
EDA is a pattern where systems communicate by reacting to events. Events are captured and consumed asynchronously.
Real-World Example:
- Uber uses EDA for real-time ride updates.
- Amazon uses EDA to update stock inventory after purchase.
C# Example (Event Handler):
public class OrderPlacedEvent
{
public int OrderId { get; set; }
public DateTime Time { get; set; }
}
public class OrderHandler
{
public void Handle(OrderPlacedEvent evt)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Order {evt.OrderId} placed at {evt.Time}");
}
}
10. EDI (Electronic Data Interchange)
What it is:
EDI enables businesses to exchange documents (purchase orders, invoices) electronically in a standardized way.
Real-World Example:
- Walmart suppliers send invoices via EDI.
- Shipping and logistics companies automate orders with EDI.
C# Example (Simulated EDI XML Processing):
using System.Xml.Linq;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
var edi = new XElement("Invoice",
new XElement("OrderId", "1234"),
new XElement("Amount", "2500"));
Console.WriteLine(edi);
}
}
11. SSE (Server-Sent Events)
What it is:
SSE allows a server to push continuous updates to the client over a single HTTP connection. Unlike WebSockets, communication is one-way (server → client).
Real-World Example:
- Stock tickers streaming updates.
- News feeds pushing live headlines.
C# Example (ASP.NET Core SSE Endpoint):
[HttpGet("sse")]
public async Task Stream(CancellationToken ct)
{
Response.ContentType = "text/event-stream";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
await Response.WriteAsync($"data: Update {i}\n\n");
await Response.Body.FlushAsync();
await Task.Delay(1000, ct);
}
}
🔑 Abhishek’s Take
APIs are no longer just about data exchange; they define how modern applications interact, scale, and innovate. From REST to gRPC, from EDA to MQTT, choosing the right protocol depends on use case, performance needs, and ecosystem fit.
👉 For developers: Start with REST/GraphQL, then explore WebSockets, MQTT, and gRPC for advanced real-time and microservice scenarios.
👉 For architects: Think of API communication styles as building blocks — the right mix ensures performance, scalability, and seamless integration.
#APIs #Developers #Microservices #IoT #CloudComputing #SystemDesign #Architecture #Azure #CSharp #GraphQL #RESTAPI #gRPC #FirstCrazyDeveloper

Leave a comment